Describe Alpha Beta and Gamma Radiation
There are four major types of radiation. The alpha-beta model is a mathematical equation used to describe the velocity of fatigue crack growth da dN as a function of a constant amplitude load driving force ΔK where its constants α and β are obtained through a.
Unlike alpha and beta particles which have both energy and mass gamma rays are pure energy.
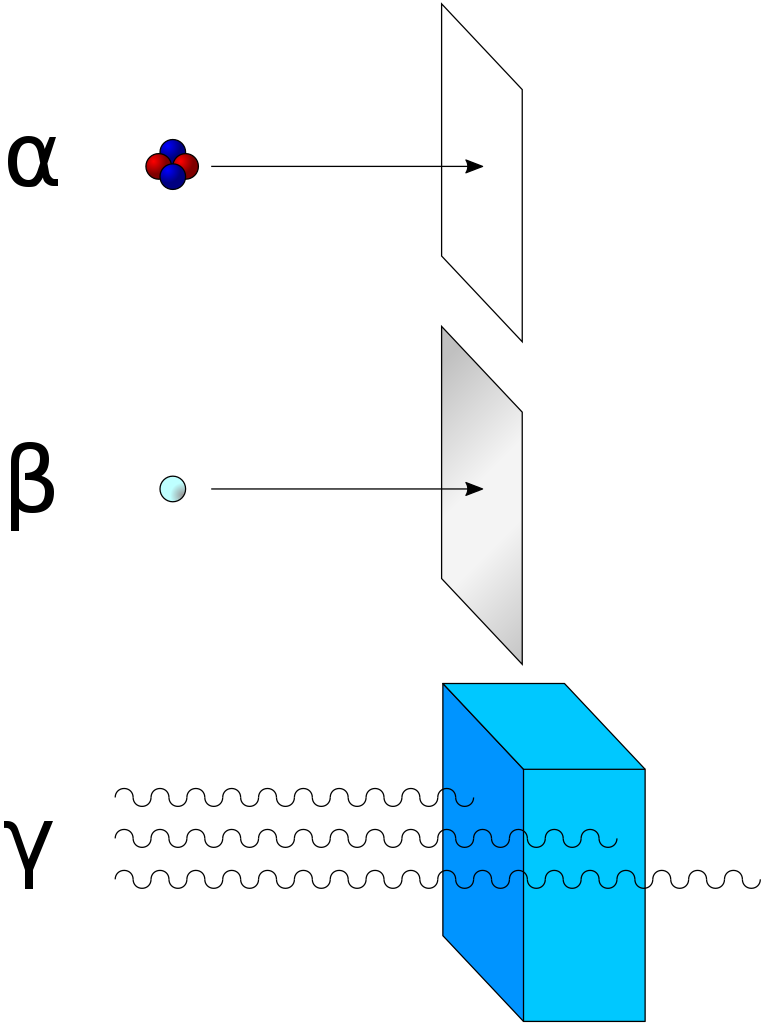
. Gamma rays are a radiation hazard for the entire body. The production of alpha particles is termed alpha decay. Beta and alpha radiation are examples of particulate radiation.
Prepare a 700- to 1050-word paper in which you analyze the effects of ionizing radiation on DNA to provide a chemical reason as to why this might cause cancer. Alpha beta gamma By a sheet of aluminum 1 cm thick. Describe how the changes in DNA may.
Medical imaging and radiotherapy. As mentioned radiation doesnt have to be electromagnetic. Smoke from a fire absorbs alpha radiation altering the ionisation and triggering the alarm.
During radioactivity particles like alpha. Ionizing radiation can also be produced by devices such as X-ray machines. Alpha radiation can be described as the producer of high energy and fast moving helium particles.
Ionisation is useful for smoke detectors. Alpha Beta and Gamma Radiation Alpha radiation consists of alpha particles that are energetic nuclei of helium. Describe the chemistry of DNA.
Beta radiation is used for tracers and monitoring the thickness of. Irradiation occurs when all or part of the body is exposed to radiation from a source. The first is an alpha particle.
6 rows Properties of Alpha Beta and Gamma Rays. It can be stopped or absorbed by a sheet of paper. Alpha particles have a charge of from its two.
They differ in mass energy and how deeply they penetrate people and objects. Ionizing radiation may be characterized further as alpha beta or gamma radiation by its behavior in a magnetic field. What is the penetrating power and ionizing power of gamma radiation.
Beta radiation is the producer of fast moving electrons and can penetrate further in comparison to the alpha particles. The alpha and. These particles consist of two protons and two neutrons and are the heaviest type of radiation particle.
Uses of beta radiation. Difference between Alpha Beta and Gamma Radiation Key Difference. Gamma rays are similar to visible light but have much higher energy.
The alpha beta and gamma radiations are the types of nuclear radiation. These radiation products include helium ions alpha radiation electrons and positrons beta radiation and photons gamma radiation. In physics gamma rays γ-rays are a kind of radiation that result from nuclear decay.
Beta Used in thickness measurement very thin things medical radiotherapy etc. Substances that give out radiation are said to be radioactive. What is alpha beta in maths.
Radioactive americium releases alpha radiation which ionises the air inside the detector. When atoms decay they emit three types of radiation alpha beta and gamma. Alpha beta neutrons and electromagnetic waves such as gamma rays.
8 rows Charge of Alpha Beta and Gamma Radiation. The gamma ray is not deflected by a magnetic field which demonstrates that unlike the alpha and beta rays the gamma is not a stream of charged particles but is electromagnetic radiation. How dangerous The bottom line is NUCLEAR RADIATION can be a Danger and also a tool.
The RBE of alpha radiation is. Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus. Include the following items.
Nuclear radiation There are three main types of ionising radiation emitted from the unstable nuclei of radioactive atoms - these are alpha beta and gamma radiation. These sources produce extremely high energy radiation hence their notoriety for being harmful and dangerous. Explain the effects of radiation on the DNA sequence.
Radioactivity Alpha Beta and Gamma Alpha Beta and Gamma Nuclear radiation comes from the nucleus of an atom. Gamma rays are often emitted along with alpha or beta particles during radioactive decay. A quantum particle usually released from radioactive decay after alpha or beta decay has occurred and the atom is still in an excited state.
Uses of alpha radiation. Describe alpha beta and gamma radiation. Gamma sterilising killing thickness measurement in metals.
An extremely high-energy photon photon particle of light. Alpha beta gamma b Which would cause the greatest biological damage if 10 rad were ingested or inhaled. Alpha Beta and Gamma Radiation Emissions from radioactive nuclei are called collectively ionizing radiation because collision between these emissions and an atom or molecule ionizes that atom or molecule.
A Which types of radiation can be blocked by a sheet of paper. The alpha radiation transfers more energy to an absorber than beta or gamma radiation. Alpha beta gamma Alpha radiation Alpha radiation is the least penetrating.
Irradiation refers to exposure to radiation. There are three types of nuclear radiation. Gamma radiation and X-rays are examples of electromagnetic radiation.
Alpha radiation emits a helium atom alpha particle having. Alpha Used in smoke alarms as an example.
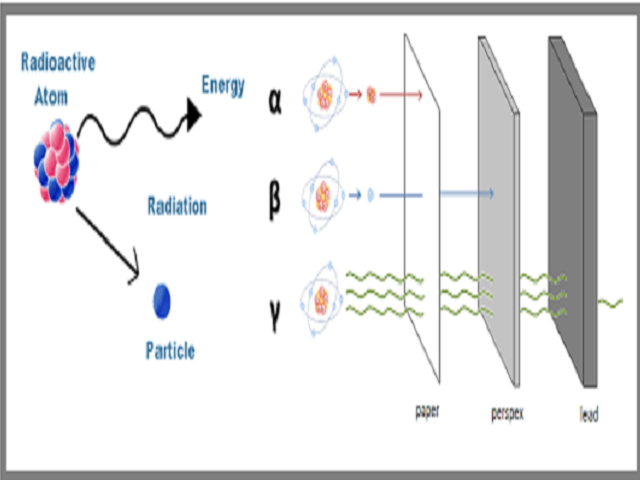
What Is The Difference Between Alpha Beta And Gamma Rays

Berkas Alfa Beta Gamma Radiation Svg Wikipedia Bahasa Indonesia Ensiklopedia Bebas
Berkas Alfa Beta Gamma Radiation Penetration Svg Wikipedia Bahasa Indonesia Ensiklopedia Bebas
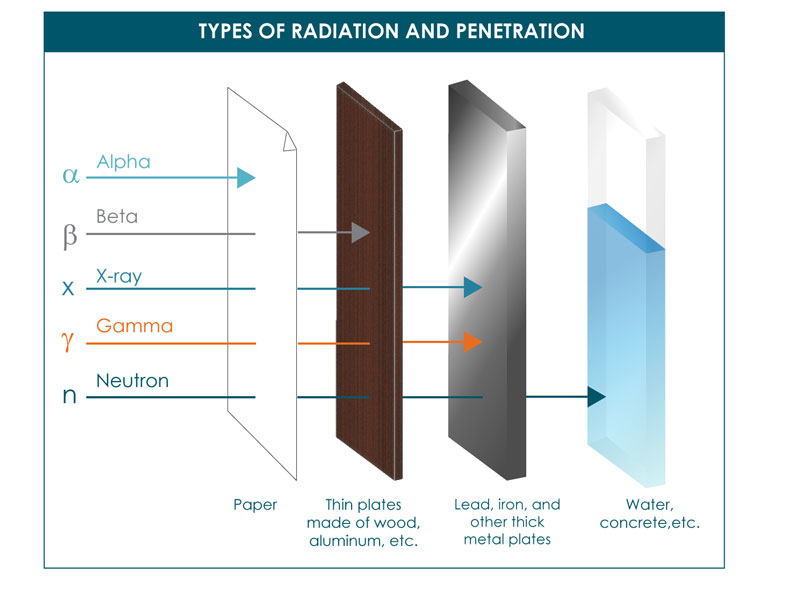
No comments for "Describe Alpha Beta and Gamma Radiation"
Post a Comment